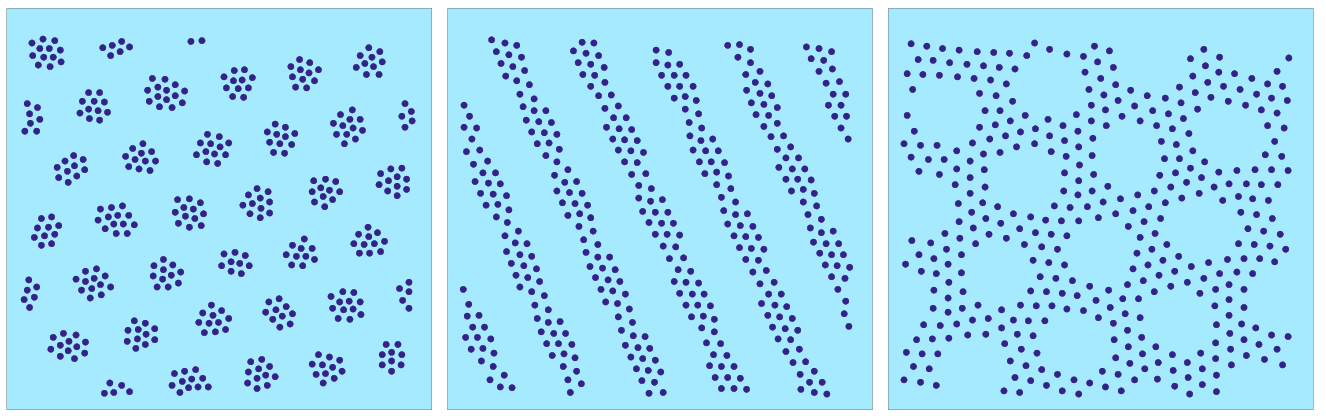
Competing long-range/short-range interactions
Two-dimensional systems in which there is a competition between
long-range repulsion and short range attraction exhibit a
remarkable variety of patterns such as stripes, bubbles,
and labyrinths.
Such systems include magnetic films,
Langmuir monolayers, polymers, gels, and water-oil mixtures.
It has been proposed that similar competing interactions
can arise in two-dimensional electron systems leading to
stripes, clumps, and liquid crystalline electron
states. Stripe and other charge-ordered phases
in metal oxides are sometimes modeled as systems with competing long
range repulsion and short range attraction.
In many of these systems quenched disorder from the underlying
substrate may be present; however, it is not known how this disorder
would affect the structure and dynamics of these systems.
Quenched disorder can strongly alter the transport properties,
producing a pinning effect in
which a finite driving force must be applied before net motion occurs.
Preprints:
-
Ratchet effects in cyclic pattern formation systems with competing interactions
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Ratchet effects can appear for particles interacting with an asymmetric potential under ac driving or for a thermal system in which a substrate is periodically flashed. Here, we show that a new type of collective ratchet effect can arise for a pattern-forming system coupled to an asymmetric substrate when the interaction potential between the particles is periodically oscillated in order to cycle the system through different patterns. We consider particles with competing short-range attraction and long-range repulsion subjected to time-dependent oscillations of the ratio between the attractive and repulsive interaction terms, which causes the system to cycle periodically between crystal and bubble states. In the presence of the substrate, this system exhibits both a positive and a reversed ratchet effect, and we show that there is a maximum in the ratchet efficiency as a function of interaction strength, ac drive frequency, and particle density. Our results could be realized for a variety of pattern-forming systems on asymmetric substrates where the pattern type or particle interactions can be oscillated.
arXiv
Papers:
-
Driven probe particle dynamics in a bubble forming system
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
J. Chem. Phys. 163, 094903 (2025).
arXiv
-
Active microrheology and dynamic phases for pattern forming systems with competing interactions
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Phys. Rev. E 111, 055406 (2025).
arXiv
-
Directional locking and hysteresis in stripe and bubble forming systems on one-dimensional periodic substrates with a rotating drive
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Phys. Rev. E 111, 054119 (2025).
arXiv
-
Stripe and bubble ratchets on asymmetric substrates
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 043290 (2024).
arXiv
-
Peak effect and dynamics of stripe and pattern forming systems on a periodic one dimensional substrate
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Phys. Rev. E 109, 054606 (2024).
arXiv
-
Sliding dynamics for bubble phases on periodic modulated substrates
C. Reichhardt and C.J.O. Reichhardt
Phys. Rev. Res. 6, 023116 (2024).
arXiv
-
Structural transitions and hysteresis in clump- and stripe-forming systems under
dynamic compression
D. McDermott, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and C. Reichhardt
Soft Matter 12, 9549 (2016). arXiv
-
Stripe systems with competing interactions on quasi-one-dimensional
periodic substrates
D. McDermott, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and C. Reichhardt
Soft Matter 10, 6332 (2014). arXiv
-
Ordering of colloids with competing interactions on quasi-one-dimensional
periodic substrates
C. Reichhardt, D. McDermott, and C.J. Olson Reichhardt
Proc. SPIE 9164, Optical Trapping and Optical Micromanipulation XI,
916420 (2014).
-
Static and dynamic phases for magnetic vortex matter with attractive
and repulsive interactions
J.A. Drocco, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 345703 (2013).
-
Statics and dynamics of vortex matter with competing repulsive and
attractive interactions
C. Reichhardt, J. Drocco, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 2041 (2013). arXiv
-
The effect of pinning on vortex states with attractive and repulsive interactions
C. Reichhardt, J. Drocco, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Physica C 479, 15 (2012).
-
Statics and dynamics of wetting-dewetting transitions for particles with
attractive interactions on periodic substrates
J.A. Drocco, C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Proc. SPIE 8458, Optical Trapping and Optical Micromanipulation IX,
84581J (2012).
-
Anisotropic sliding dynamics, peak effect, and metastability in stripe systems
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Phys. Rev. E 83, 041501 (2011). arXiv
-
Structural transitions, melting, and intermediate phases for stripe- and
clump-forming systems
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Phys. Rev. E 82, 041502 (2010). arXiv
-
Commensurate and incommensurate checkerboard charge ordered states
C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Physica C 460-462, 1178 (2007).
-
Noise and hysteresis in charged stripe, checkerboard, and clump forming
systems
C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Proc. SPIE 6600, Noise and Fluctuations in Circuits, Devices, and Materials,
66001B (2007).
-
Structure and fragmentation in colloidal artificial molecules and
nuclei
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Eur. Phys. J. E 22,11 (2007). arXiv
-
Hysteresis and noise in stripe- and clump- forming systems
C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Europhys. Lett. 72, 444 (2005). arXiv
-
Dynamics and melting of stripes, crystals, and bubbles with
quenched disorder
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, I. Martin, and A.R. Bishop
Physica D 193, 303 (2004). arXiv
-
Fibrillar templates and soft phases in systems with short-range
dipolar and long-range interactions
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, and A.R. Bishop
Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 016801 (2004). arXiv
-
Effect of field-effect transistor geometry on charge ordering of
transition-metal oxides
C.J. Olson Reichhardt, C. Reichhardt, D.L. Smith, and A.R. Bishop
Phys. Rev. B 68, 033101 (2003). arXiv
-
Dynamical ordering of driven stripe phases in quenched disorder
C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson Reichhardt, I. Martin, and A.R. Bishop
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 026401 (2003). arXiv
-
Depinning and dynamics of systems with competing interactions in
quenched disorder
C. Reichhardt, C.J. Olson, I. Martin, and A.R. Bishop
Europhys. Lett. 61, 221 (2003). arXiv
Last modified November 16, 2016
